After 20 years of applying an obsolete system for the valuation of damages caused to people in traffic accidents, on 1st January 2016, a new system came into force (Law 35/2015, of 22nd September, reforming the system for the valuation of damages caused to people in traffic accidents) which came into force, correcting a large part of the previous one, providing us with a complex system composed of tables and concepts, based on the circumstantial casuistry that could occur in the victims.
The system advocates, this time more correctly, as fundamental principles:
1. Principle of full reparation: it assumes full indemnity for the damages caused.
2. Principle of articulation: it requires that patrimonial and non-patrimonial loss be assessed separately and, within each other, the different concepts.
What elements make up the compensation
First of all, it is important to recognise all the items included in the Schedule to compensate those damages which, consequently, are liable for compensation.
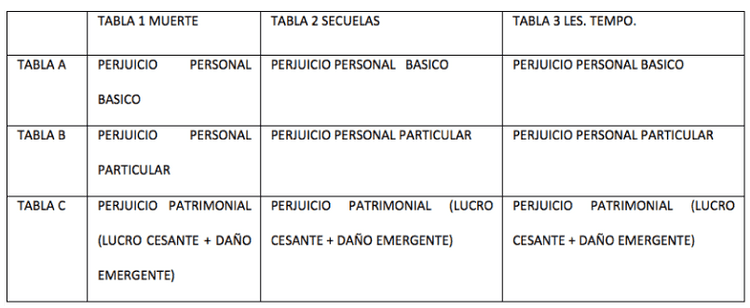
The structure of the Schedule is clear, concrete and simple, leaving little room for discretion, offering a method of compensation that starts with whether, after the traffic accident, the object of assessment is death, permanent incapacity or sequelae or temporary incapacity. In each of them, there are 3 concepts that are the object of compensation; the basic personal injury, the particular personal injury and the patrimonial loss. Below we show the structure of the Schedule.

CALCULATION OF COMPENSATION FOR PERSONAL INJURY IN CASES OF TEMPORARY DISABILITY AND SEQUELAE
This section will focus on the calculation of compensation in situations 2 and 3, after-effects and temporary disability. The case of death, due to its complexity, will be dealt with in a separate post later on.
- TEMPORARY INCAPACITY. WE TURN TO TABLES 3.A, 3.B and 3.
Table 3 (A, B and C) values the damage caused within the period from the time of the accident until the date of injury stabilisation or medical discharge, whether personal, assigning an amount per day depending on whether it is classified as basic, moderate, serious or very serious. And patrimonial, depending on the amounts that are accredited as having been borne.

-AFTEREFFECTS or SEQUELAE. Tables A, 2. B and 2.
Sequelae are the physical, intellectual, organic and sensory impairments and aesthetic damage that derive from an injury and remain after the healing process is complete. And for this, we turn to Table 2:
TABLE 2.A.1 corresponds to the medical scale, and the BASIC PERSONAL INJURY.

Locate the sequela in question within the Medical Scale, and observe that a range appears for each one of them. This is the score that corresponds to that sequela, and within which the corresponding number of points will be assigned.
Once the score has been assigned, we turn to the following table.
TABLE 2.A.2. ECONOMIC SCALE

This table, which is easy to apply, shows the economic valuation of our injuries, according to the number of points assigned to the specific injury and according to the age of the injured person.
TABLE 2.B. PARTICULAR PERSONAL INJURY

Table 2.B, will be used only in those cases in which the sequela suffered exceeds a certain number of points. It is a table that compensates in an extra way those cases in which the damages are of greater severity.
TABLE 2.C. PECUNIARY DAMAGE or PATRIMONIAL LOSS

Table 2.C guarantees compensation for present and future pecuniary damage, if any, caused to the injured party.
And finally, a simple example:
A 31-year-old male cook with 2 sequelae and 95 days of temporary incapacity, 30 of which he was on sick leave, during which time he received his full salary.
We turn to Table 3 to quantify the period of temporary incapacity, i.e. the number of days. In this sense, 30*64.25 and 65*37.06 = 4,336.4 euros.
On the other hand, we turn to Table 2, first to the medical scale to identify our sequela, then to the economic scale to quantify it. In this way, we extract that a person of 31 years of age with two points of sequela corresponds to 2,073.93 euros.
Since in our example there are no other damages, the total amount to be compensated is 6,410.33 euros.