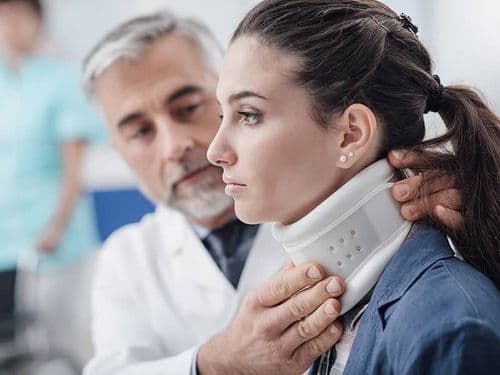
When you are in the process of claiming compensation, sometimes differences arise between the insurance expert's and the victim's version of the extent of the injuries. In these cases, it is possible to request the intervention of a forensic surgeon to examine the injured person and make a report. The role of this forensic report in a traffic accident is very valuable, as it is able to relate the injuries and after-effects that a person has to what happened in an accident.
Until 2016, the only way to obtain a forensic report free of charge was if the road traffic accident was being investigated in criminal proceedings. However, since the entry into force of Royal Decree 1148/2015 of 18th December, any victim of a car accident has the possibility of requesting a forensic report free of charge and out of court to prove the extent of their injuries.
So if you are currently processing a claim for compensation for a traffic accident, here we explain everything you need to know about the forensic report.
What a forensic report is and why it is important
A forensic report is a document that links the injuries sustained by a person to what happened in a traffic accident. For this, the medical surgeon takes as a reference the tests that have been carried out on the victim, the injuries diagnosed and the rehabilitation period needed to recover from them. In addition, the forensic report also includes the functional, psychological or aesthetic sequelae of the injured person once rehabilitation has been completed.
This report is an objective document, since:
- Both parties, the injured party and the insurer, have the right to request that any aspect they consider appropriate be included in the report.
- Neither the victim nor the insurer can choose the forensic surgeon who will carry out the examination and the report.
- The same doctor is never assigned by default to cases from the same insurer.
Therefore, the forensic report is essential because:
- It allows the compensation calculators to better quantify the extent of the injuries.
- It helps the injured party to obtain a fairer compensation in accordance with the damages suffered.
- In the event of having to go to court, the forensic report provides the court with more precise and detailed information, from a scientific and medical point of view, about the events that occurred.
Getting a forensic report?
To obtain a forensic report, it is necessary to submit a request to the Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences of the place where the accident took place or where the victim's home is located.
The request can be made by the injured party, the insurance company or both parties by mutual agreement. However, when it is the insurance company that requests this report, it must have the authorisation of the victim.
Together with the application, the following documents must be submitted:
- The reasoned offer presented by the insurer.
- The medical documentation that the injured person has and that issued by the insurer.
- Any other documentation, photographs, reports, etc., that may be useful.
Before accepting the application, if the Institute of Legal Medicine notices any error or mistake, it can require that it be rectified within 10 days. If everything is correct, it will summon the injured person for the examination and will inform the insurer.
During the month following the examination, both the victim and the insurance company will receive the report from the forensic institute and both will have seven days to request any clarification or correction they consider appropriate.
Contents of the forensic report?
The forensic report serves as a basis for the insurer to submit a second reasoned offer or for the victim to decide to initiate a legal claim, therefore it should include the following information:
- The details of the injured person, the insurance company and the forensic surgeon who prepared the report.
- An explanation of the circumstances in which the accident occurred and the most relevant details and facts of the accident.
- The examinations, tests and other assessments carried out on the injured person during the period of medical care that have been taken into account in the report.
- A detailed explanation of the extent of the injuries suffered by the victim, the after-effects and any other damage that the victim may suffer for life.
- The place, date and time of the examination.
Who assumes the costs of the forensic report in a compensation claim?
It will be the insurer of the vehicle responsible for the accident who will be responsible for paying the cost of the forensic report, never the injured party.
However, if the insurance company denies the responsibility of its insured in the accident or it is demonstrated that there is no relation between the accident and the injuries of the victim, or that these are of lesser severity; the intervention of a forensic surgeon cannot be requested.
The alternative is for the injured party to go to a private medical expert and pay for the report out of pocket in order to be able to file a lawsuit against the insurer. In this case, if necessary, this expert can later go to court to ratify his report, unlike the forensic doctor.
How are the damages quantified in the case of a civil claim?
In order to initiate a civil claim, all the damages suffered by the victim as a result of the traffic accident must be quantified. This quantification is made on the basis of the medical expert's report and the provisions of the accident scale.
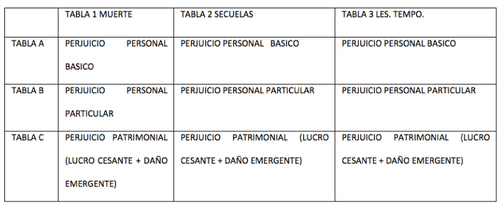
For the calculation of damages, a distinction must be made between:
- Basic personal injury. Here compensation is paid:
- The death of the victim.
- Temporary injuries, depending on the number of days it has taken to heal and the loss of quality of life during this time.
- The after-effects or sequelae, according to the level of help needed for personal autonomy.
- The particular personal injury. In this case, the specific circumstances of the injured party are taken into account to establish an amount.
- The pecuniary damage. Here it is necessary to differentiate:
- Loss of earnings or loss of income of the injured party.
- Emerging damage or expenses derived from the accident.
Can the insurer lower the amount of the reasoned offer if the expert examination indicates fewer injuries?
In the event that the forensic surgeon in his report assesses that the victim has fewer injuries and/or sequelae than the insurer's expert in his documentation indicates, the insurance company should not lower the amount of compensation proposed in the reasoned offer. If it did so, it would be acting against the information that it itself has used and provided.
However, it is not very common for the coroner's examination to determine that the victim's injuries are less than what is reflected in the previous medical documentation. In any case, to avoid this, it is advisable to accept the reasoned offer as payment on account and then request the forensic medical report.
If the reasoned offer is accepted, do I lose my right to make a claim out of court?
Not in any case. The acceptance by the victim of the amount proposed by the insurer in the reasoned offer is not a waiver of his or her right to continue claiming, out of court or in court, a fairer amount to compensate for the injuries and damages he or she has suffered in a traffic accident.
Therefore, after acceptance of the reasoned offer, the insurance company cannot require the claimant to sign any kind of waiver document.
How much does a medical expert's consultation cost and who has to pay for it?
If the victim of a traffic accident cannot request the free forensic report, for the reasons given above, then he or she will have to go to a private medical expert if he or she wants to continue with the claim for compensation. In this case, as it is a personal decision, the claimant will have to pay the cost of the report out of pocket.
How much it costs to consult a private medical expert and obtain a report depends on the individual professional. We therefore recommend that you seek the advice of a lawyer specialising in compensation claims, as skimping on this can be counter-productive.
Which doctors can issue an expert report
In principle, Spanish law stipulates that any medical graduate can produce an expert report. However, not all doctors do so. Doctors with clinical specialties, although they have the capacity to give an expert opinion on any health or scientific issue, have been trained to diagnose and treat patients.
Therefore, a judge will always give more credibility to a doctor who specialises in forensic and legal medicine, and not all medical experts are.
What to consider when hiring one
Choosing the right medical expert is essential if you want to get a fair road traffic accident compensation. Here are some of the considerations you should take into account when hiring one:
- It is important that they do not work for any insurance company or assistance service linked to them, as in that case they cannot produce expert reports.
- You have to take into account both their professional career and prestige, as well as their training, as not all experts are specialists in legal and forensic medicine.
- Ideally, they should transmit confidence from the outset.
- In the event that you have to go to court, it is good that you have a certain amount of experience and that he or she has the communication skills to specify, defend and explain your opinion, as well as the ability to respond and improvise.
Importance of the medical history in expert evidence
In a claim for compensation for a traffic accident, it is up to the victim to prove what happened and for this, the medical history is essential because it is the basis on which expert evidence is carried out.
The medical history is the set of medical documents that have been generated as the injured person has received medical care after the accident with the aim of healing or stabilising their injuries. For this reason, they are undoubted proof of the injuries, diagnosis and treatment received by the injured party in an accident.
The more complete the medical records provided by the claimant in his or her claim against the insurer, the better the chances of obtaining a fair compensation. Thanks to it, your lawyer will be able to defend your position better and the judge will have objective information to reconstruct the facts, to check if the damage caused could have been avoided, to determine if there are any after-effects and how they will affect your life, etc.